Enjoy!
Reference
https://festivetechcalendar.com/
This week, Microsoft announced the public preview of geo-replication for Azure Event Hubs. Geo-replication enhances Microsoft Azure data availability and geo-disaster recovery capabilities by enabling the replication of Event Hubs data payloads across different Azure regions.
With geo-replication, your client applications continue to interact with the primary namespace. Customers can designate a secondary region, choose replication consistency (synchronous or asynchronous), and set replication lag for the data. The service handles the replication between primary and secondary regions. If a primary change is needed (for maintenance or failover), the secondary can be promoted to primary, seamlessly servicing all client requests without altering any configurations (connection strings, authentication, etc.). The former primary then becomes the secondary, ensuring synchronization between both regions.
In summary, geo-replication is designed to provide you with the following benefits:
If you want to try out Azure Event Hubs Geo-replication, please check out the official documentation over at Azure Event Hubs Geo-replication documentation and they also have a demo here.
I look forward to when this becomes GA and is available in more regions.
Enjoy!
Kusto, the internal service driving Microsoft’s telemetry and several key services, recently marked its 10-year milestone. Over the decade, Kusto has evolved significantly, becoming the backbone for crucial applications such as Sentinel, Application Insights, Azure Data Explorer, and more recently, Eventhouse in Microsoft Fabric. This journey highlights its pivotal role in enhancing data processing, monitoring, and analytics across Microsoft’s ecosystem.
This powerful service has continually adapted to meet the growing demands of Microsoft’s internal and external data needs, underscoring its importance in the company’s broader strategy for data management and analysis.
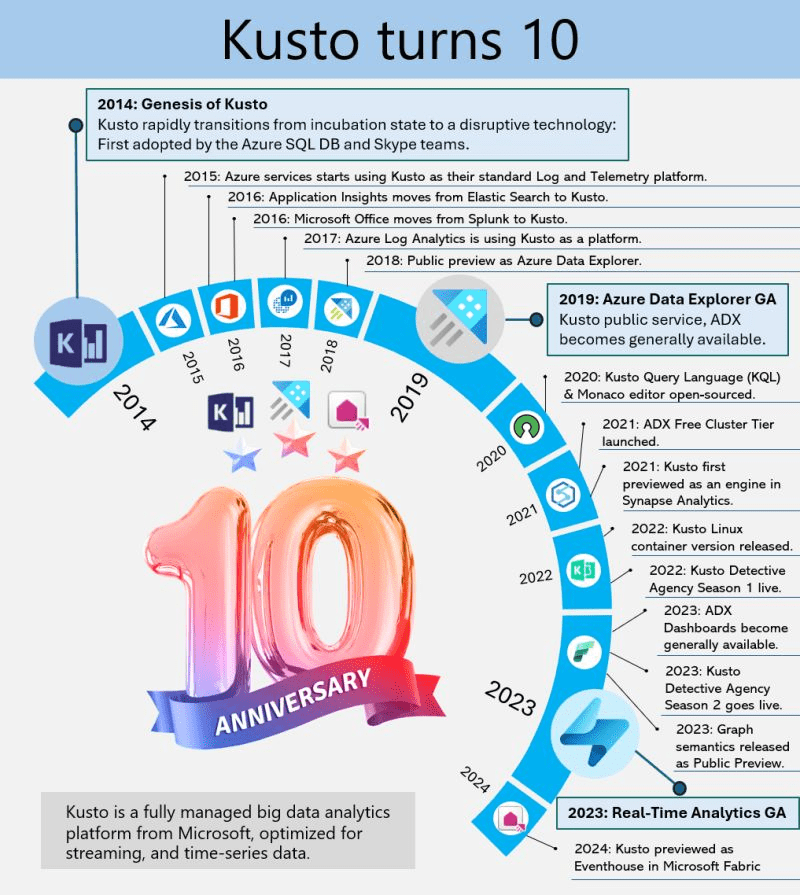
Azure Data Explorer (ADX), initially code-named “Kusto,” has a fascinating backstory. In 2014, it began as a grassroots initiative at Microsoft’s Israel R&D center. The team wanted a name that resonated with their mission of exploring vast data oceans, drawing inspiration from oceanographer Jacques Cousteau. Kusto was designed to tackle the challenges of rapid and scalable log and telemetry analytics, much like Cousteau’s deep-sea explorations.
By 2018, ADX was officially unveiled at the Microsoft Ignite conference, evolving into a fully-managed big data analytics platform. It efficiently handles structured, semi-structured (like JSON), and unstructured data (like free-text). With its powerful querying capabilities and minimal latency, ADX allows users to swiftly explore and analyze data. Remembering its oceanic roots, ADX symbolizes a tribute to the spirit of discovery.
Enjoy!
This week Microsoft announced in public preview, support for large messages (up to 20 MB) in Azure Event Hubs in its self-service scalable dedicated clusters, enhancing its capabilities to handle a wide range of message sizes without additional costs.
This new feature allows for seamless streaming of large messages without requiring any client code changes, maintaining compatibility with existing Event Hubs SDKs and the Kafka API. This enhancement ensures uninterrupted business operations by accommodating instances where messages cannot be divided into smaller segments. The service continues to offer high throughput and low latency, making it a robust solution for data streaming needs.
Here are some key use cases for the new large message support in Azure Event Hubs:
These enhancements ensure seamless and uninterrupted business operations across various scenarios.
To enable large message support in your existing Azure Event Hubs setup, follow these steps:
For more detailed instructions, visit the documentation at aka.ms/largemessagesupportforeh.
Azure Event Hubs and Event Hub Clusters serve different purposes within the Azure ecosystem:
Enjoy!
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-hubs/event-hubs-quickstart-stream-large-messages
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-hubs/compare-tiers

What is the Book of News? The Microsoft Build 2024 Book of News is your guide to the key news items announced at Build 2024.
As expected there is a lot of focus on Azure and AI, followed by Microsoft 365, Security, Windows, and Edge & Bing. This year the book of news is interactive instead of being a PDF.
Microsoft Azure Functions is launching several new features to provide more flexibility and extensibility to customers in this era of AI.
Features now in preview include:
Features now generally available include:
Microsoft Azure Container Apps will include dynamic sessions, in preview, for AI app developers to instantly run large language model (LLM)-generated code or extend/customize software as a service (SaaS) apps in an on-demand, secure sandbox.
Customers will be able to mitigate risks to their security posture, leverage serverless scale for their apps and save months of development work, ongoing configurations and management of compute resources that reduce their cost overhead. Dynamic sessions will provide a fast, sandboxed, ephemeral compute suitable for running untrusted code at scale.
Additional new features, now in preview, include:
Microsoft Azure App Service is a cloud platform to quickly build, deploy and run web apps, APIs and other components. These capabilities are now in preview:
These capabilities are now generally available:
To help customers deliver more advanced capabilities, Microsoft Azure Static Web Apps will offer a dedicated pricing plan, now in preview, that supports enterprise-grade features for enhanced networking and data storage. The dedicated plan for Azure Static Web Apps will utilize dedicated compute capacity and will enable:
Microsoft Azure Logic Apps is a cloud platform where users can create and run automated workflows with little to no code. Updates to the platform include:
An enhanced developer experience:
Expanded functionality and compatibility with Logic Apps Standard:
Microsoft Azure API Center, now generally available, provides a centralized solution to manage the challenges of API sprawl, which is exacerbated by the rapid proliferation of APIs and AI solutions. The Azure API Center offers a unified inventory for seamless discovery, consumption and governance of APIs, regardless of their type, lifecycle stage or deployment location. This enables organizations to maintain a complete and current API inventory, streamline governance and accelerate consumption by simplifying discovery.
Azure API Management has introduced new capabilities to enhance the scalability and security of generative AI deployments. These include the Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service token limit policy for fair usage and optimized resource allocation, one-click import of Azure OpenAI Service endpoints as APIs, a Load Balancer for efficient traffic distribution and a Circuit breaker to protect backend services.
Other updates, now generally available, include first-class support for OData API type, allowing easier publication and security of OData APIs, and full support for gRPC API type in self-hosted gateways, facilitating the management of gRPC services as APIs.
Microsoft Azure Event Grid has new features that are tailored to customers who are looking for a pub-sub message broker that can enable Internet of Things (IoT) solutions using MQTT protocol and can help build event-driven apps. These capabilities enhance Event Grid’s MQTT broker capability, make it easier to transition to Event Grid namespaces for push and pull delivery of messages, and integrate new sources. Features now generally available include:
The new Real-Time Intelligence within Microsoft Fabric will provide an end-to-end software as a service (SaaS) solution that will empower customers to act on high volume, time-sensitive and highly granular data in a proactive and timely fashion to make faster and more-informed business decisions. Real-Time Intelligence, now in preview, will empower user roles such as everyday analysts with simple low-code/no-code experiences, as well as pro developers with code-rich user interfaces.
Features of Real-Time Intelligence will include:
Microsoft Fabric, the unified data platform for analytics in the era of AI, is a powerful solution designed to elevate apps, whether a user is a developer, part of an organization or an independent software vendor (ISV). Updates to Fabric include:
Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB, the database designed for AI that allows creators to build responsive and intelligent apps with real-time data ingested and processed at any scale, has several key updates and new features that include:
Click here to read the Microsoft Build 2024 Book of News!
Enjoy!
For the past few months, I’ve been diving into learning Azure Data Explorer (ADX) and using it for a few projects. What is Azure Data Explorer, and what would I use it for? Great questions. Azure Data Explorer is like your data’s best friend when it comes to real-time, heavy-duty analytics. It’s built to handle massive amounts of data—whether it’s structured, semi-structured, or all over the place—and turn it into actionable insights. With its star feature, the Kusto Query Language (KQL), you can dive deep into the data for tasks like spotting trends, detecting anomalies, or analyzing logs, all with ease. It’s perfect for high-speed data streams, making it a go-to for IoT and time-series data. Plus, it’s secure, scalable, and does the hard work fast so you can focus on making more intelligent decisions.
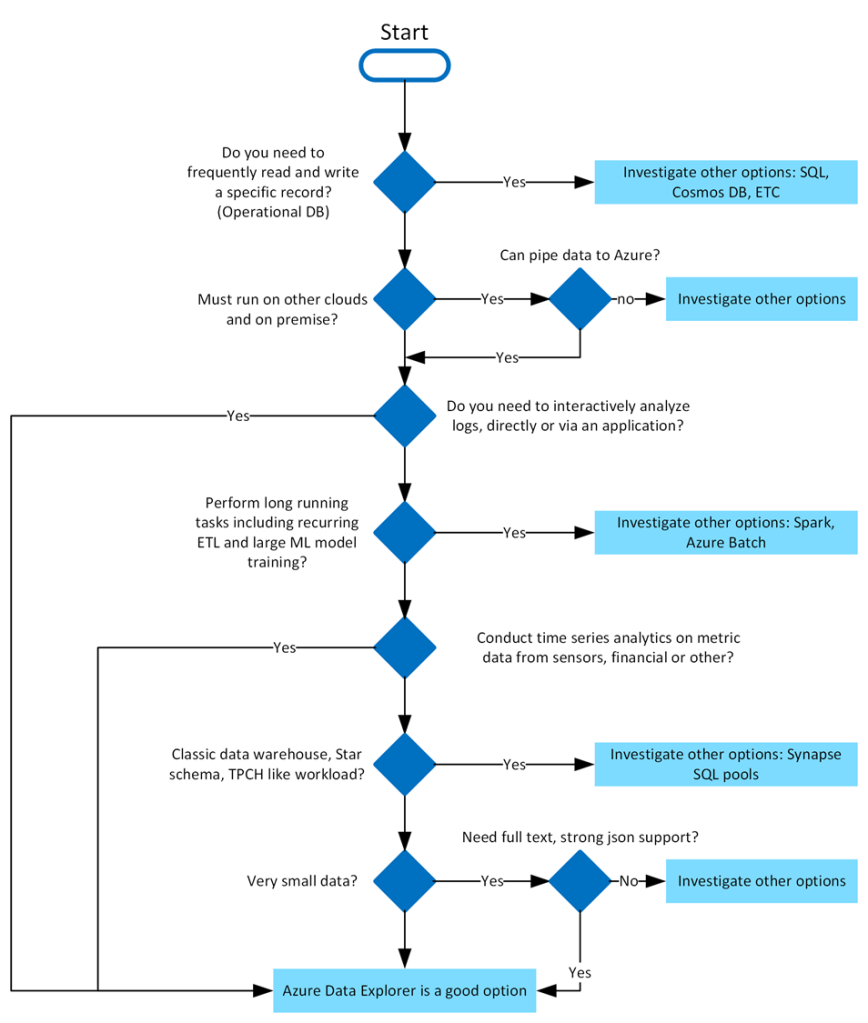
Azure Data Explorer is ideal for enabling interactive analytics capabilities over high-velocity, diverse raw data. Use the following decision tree to help you decide if Azure Data Explorer is right for you:
Azure Data Explorer stands out due to its exceptional capabilities in handling vast amounts of diverse data quickly and efficiently. It supports high-speed data ingestion (terabytes in minutes) and querying of petabytes with millisecond-level results. Its Kusto Query Language (KQL) is intuitive yet powerful, enabling advanced analytics and seamless integration with Python and T-SQL. With specialized features for time series analysis, anomaly detection, and geospatial insights, it’s tailored for deep data exploration. The platform simplifies data ingestion with its user-friendly wizard, while built-in visualization tools and integrations with Power BI, Grafana, Tableau, and more make insights accessible. It also automates data ingestion, transformation, and export, ensuring a smooth, end-to-end analytics experience.
In Azure Data Explorer, we use the Kusto Query Language (KQL) to write queries. KQL is also used in other Azure services like Azure Monitor Log Analytics, Azure Sentinel, and many more.
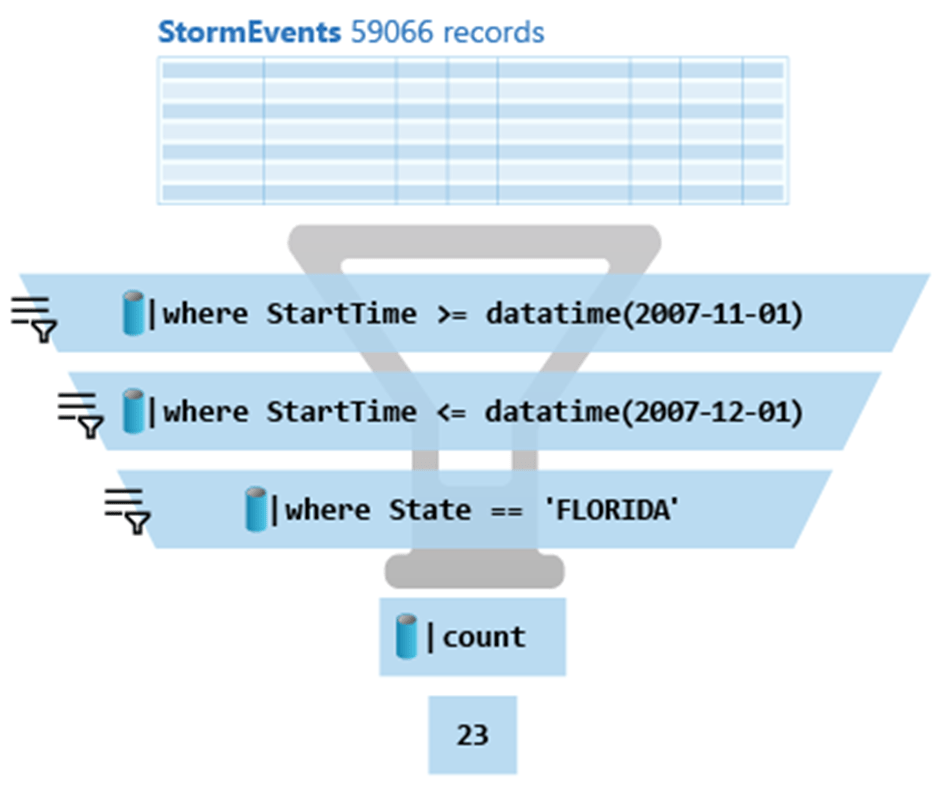
Here is the above query:
StormEvents
| where StartTime >= datetime(2007-11-01)
| where StartTime <= datetime(2007-12-01)
| where State == 'FLORIDA'
| countAzure Data Explorer query editor also supports the use of T-SQL in addition to its primary query language, Kusto query language (KQL). While KQL is the recommended query language, T-SQL can be useful for tools that are unable to use KQL. For more details, check out how to query data with T-SQL.
When it comes to writing commands for managing tables, the first character of the text of a request determines if the request is a management command or a query. Management commands must start with the dot (.) character, and no query may start with that character.
Here are some examples of management commands:
You can try Azure Data Explorer for free using the free cluster. Head over to https://dataexplorer.azure.com/ and log in with any Microsoft Account.
Navigate to the My cluster tab on the left to get access to your cluster URI.
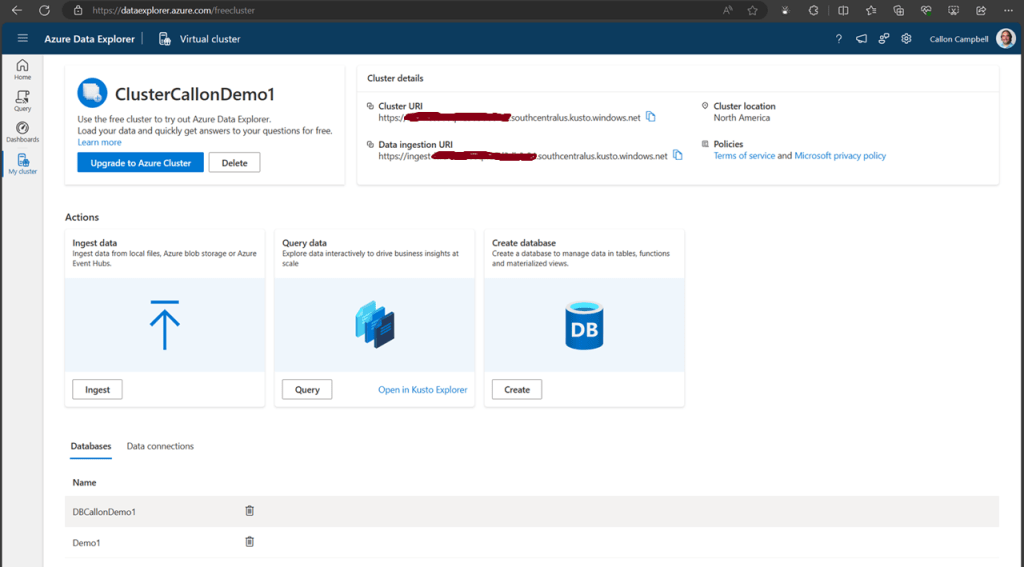
Next, let’s create a new database. While on the My cluster tab, click on the create database button. Give your database a name. In this case, I’m using ‘Demo1’ and then click on the ‘NextCreateDatebase’ button.
Now navigate over to the Query table and lets create our first table, insert some data and run some queries.
.create-merge table customers
(
FullName: string,
LastOrderDate: datetime,
YtdSales: decimal,
YtdExpenses: decimal,
City: string,
PostalCode: string
)If we run the .show table customers command, we can see the table definition:
.show table customers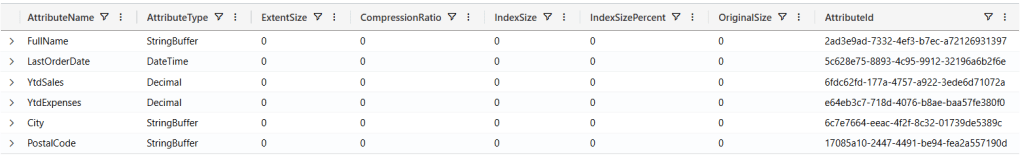
There are several ways we can ingest data into our table. Here are a few options:
Today we’re going to be using the inline ingestion, which goes as follows:
.ingest inline into table customers <|
'Bill Gates', datetime(2022-01-10 11:00:00), 1000000, 500000, 'Redmond', '98052'
'Steve Ballmer', datetime(2022-01-06 10:30:00), 150000, 50000, 'Los Angeles', '90305'
'Satya Nadella', datetime(2022-01-09 17:25:00), 100000, 50000, 'Redmond', '98052'
'Steve Jobs', datetime(2022-01-04 13:00:00), 100000, 60000, 'Cupertino', '95014'
'Larry Ellison', datetime(2022-01-04 13:00:00), 90000, 80000, 'Redwood Shores', '94065'
'Jeff Bezos', datetime(2022-01-05 08:00:00), 750000, 650000, 'Seattle', '98109'
'Tim Cook', datetime(2022-01-02 09:00:00), 40000, 10000, 'Cupertino', '95014'
'Steve Wozniak', datetime(2022-01-04 11:30:00), 81000, 55000, 'Cupertino', '95014'
'Scott Guthrie', datetime(2022-01-11 14:00:00), 2000000, 1000000, 'Redmond', '98052'Now, let’s start writing KQL queries against our data. In the following query I’m just using the name of the table with no where clause. This is similar to the “SELECT * FROM Customers” in SQL.
customers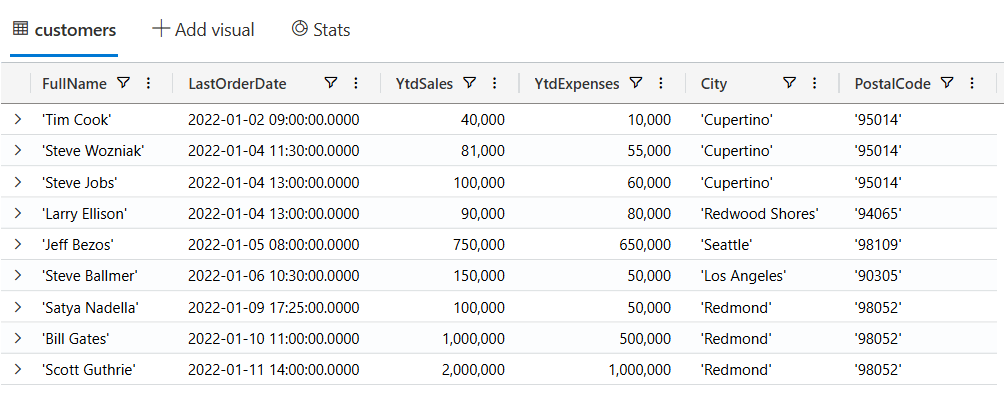
Now let’s filter our data looking for customers where the YtdSales is less than $100,000:
customers
| where YtdSales < 100000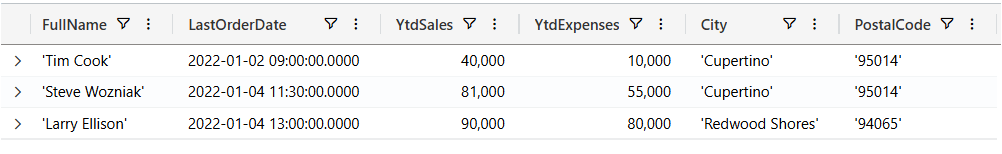
If you’re unfamiliar with KQL but are familiar with SQL and want to learn KQL, you can translate your SQL queries into KQL by prefacing the SQL query with a comment line, --, and the keyword explain. The output shows the KQL version of the query, which can help you understand the KQL syntax and concepts. Here is an example of the ‘EXPLAIN’ operator as follows:

Try the SQL to Kusto Query Language cheat sheet.
In this post we looked at what Azure Data Explorer is, when it should be used, how to use the free personal cluster to create a sample database and ingest data and the run some queries. I hope this was insightful and I look forward to my next post where I’ll go deeper on ingesting data in real-time and running more complicated queries and how we can access this data from dashboards and APIs.
Enjoy!
Earlier this week, Microsoft announced that it would follow suit with Google and Amazon in eliminating Azure egress fees. The following outlines Azure’s commitment to customer choice and details the process for transferring data out of Azure with financial incentives.
Azure now provides free data egress for customers leaving Azure, allowing them to transfer their data to another cloud provider or on-premises data center without incurring internet fees.
The first 100GB/month is free globally. For additional data transfer, customers must contact Azure Support and follow specific instructions to be eligible for the credit.
Once the data transfer is complete and all associated Azure subscriptions are cancelled, Azure Support will apply the credit.
This policy aligns with the European Data Act and is available to all Azure customers worldwide.

What is the Book of News? The Microsoft Ignite 2023 Book of News is your guide to the key news items that are announced at Ignite 2023.
AI, Copilot and Microsoft Fabric will have an overarching theme at this year’s conference as you will see throughout the sessions and announcements.
Azure IoT Operations is a new addition to the Azure IoT portfolio that will offer a unified, end-to-end Microsoft solution that digitally transforms physical operations seamlessly from the cloud to the edge.
That unified approach consists of the following:
Learn more about Accelerating Industrial Transformation with Azure IoT Operations
Azure Chaos Studio, now generally available, provides a fully managed experimentation platform for discovering challenging issues through experiment templates, dynamic targets and a more guided user interface.
This year’s Ignite was packed with lots of new announcements and features that I can’t wait to start using in my applications.
Enjoy!

What is the Book of News? The Microsoft Build 2023 Book of News is your guide to the key news items that are announced at Build 2023.
As expected there is a lot of focus on Azure and AI, followed by Microsoft 365, Security, Windows, and Edge & Bing. This year the book of news is interactive instead of being a PDF.
These updates are now in preview. Learn more about public preview of MQTT protocol and pull message delivery in Azure Event Grid.
Azure Communication Services
Click here to read the Microsoft Build 2023 Book of News!
Enjoy!

In this episode of Azure Friday, Amar Gowda joins Scott Hanselman to show how Azure Confidential Computing protects data in use and helps you achieve data security and data privacy goals within a managed cloud environment. Confidential VM’s protect VM-based workloads with memory encryption and code integrity for VM and container workloads. Attestation helps you remotely verify the entire VM is a hardware-based Trusted Execution Environment (TEE).
Source: Azure Friday
A French word, a photo, and a slice of life in Provence
Microsoft MVP on Azure IoT & Real-Time Intelligence | International Speaker | Principle architect at Alten-SDG Group
It's all about Microsoft Business Applications
AI & Cloud Consulting for Modern Enterprises
Author: John Lunn @jonnychipz
If you're not having fun, you're doing it wrong.
Code. Fun. Serverless
Intelligent Apps for Pilots
My personal blog about everything technical
coding facts and opinions
Sponsored by Cloud Formations Ltd
Exploring the world of Azure, IoT and other interesting topics
where learning never ends...
Practical Coding Tutorial
A blog about Microsoft Azure
Christian Nagel and the CN innovation team about .NET Aspire, C#, Azure, ASP.NET Core, WinUI, .NET MAUI, and more
Cloud Computing & DevOps Tips & Tricks with Hammad Aslam.